Morton’s Neuroma Relief
Morton’s Neuroma is a painful foot condition affecting many people. Treatment options are available at Casteel Foot & Ankle Center in Rowlett, TX. If you are suffering from Morton’s neuroma, Dr. Casteel, DPM, and her team are ready to help you become pain-free.
What is Morton’s Neuroma?
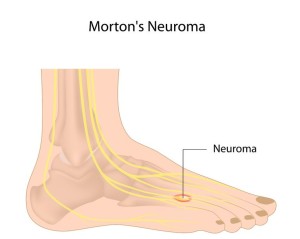 Morton’s neuroma affects the ball of the foot between the third and fourth toes. It is an injury to the nerve between the toes, causing a thickening of the tissue around the nerve. In many cases, this heel disorder may feel like a pebble in your shoe. In women, the condition is more likely for those who wear high-heeled shoes. Some causes of Morton’s neuroma are:
Morton’s neuroma affects the ball of the foot between the third and fourth toes. It is an injury to the nerve between the toes, causing a thickening of the tissue around the nerve. In many cases, this heel disorder may feel like a pebble in your shoe. In women, the condition is more likely for those who wear high-heeled shoes. Some causes of Morton’s neuroma are:
Symptoms of Morton’s neuroma may include:
- Cramping of toes
- Shooting or burning pains in the ball of the foot or toes
- Pressure on the affected area
- Tingling in the area
- Increased pain over time
Wearing restrictive or tight shoes causes pressure on the enlarged nerve when walking, resulting in compression of the area causing pain as the nerve is squeezed.
Morton’s Neuroma Treatment
Treatment for Morton’s neuroma involves nonsurgical approaches as well as surgical options. The foot pain specialist will first give a full examination and determine the extent of the condition. Nonsurgical options may include:
- Shoe inserts
- Custom Orthotics
- Taping toes or padding
- Changing shoes
- Pain medication to reduce inflammation
- Injections to area
- Physical Therapy
Foot surgery is available if nonsurgical options are non-responsive. Surgery may include removing the thickened tissue and rehabilitation.
Call for Morton’s Neuroma Treatment
Call Casteel Foot and Ankle Center at 972-412-4449 or contact us online to make an appointment to treat Morton’s neuroma. Dr. Casteel, DPM and her team will ensure you receive the best available care. Our office is centrally located in Rowlett, TX serving the community and surrounding area.
